Due to differences in rules at the University of South Bohemia in České Budějovice and Johannes Kepler University in Linz Organisation of joint master state exam in Biological Chemistry had to be adjusted.
The state exam will be located at the institution where the student worked on his/her diploma thesis and will have two parts:
1) Master thesis defence
2) Oral exam consisting of
- Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (Biology-oriented part of the exam)
- General Chemistry (Chemistry-oriented part of the exam)
- Elective subject (subject related to the topic of master thesis)
See below for additional information.
Additional information for students working on their theses in Linz:
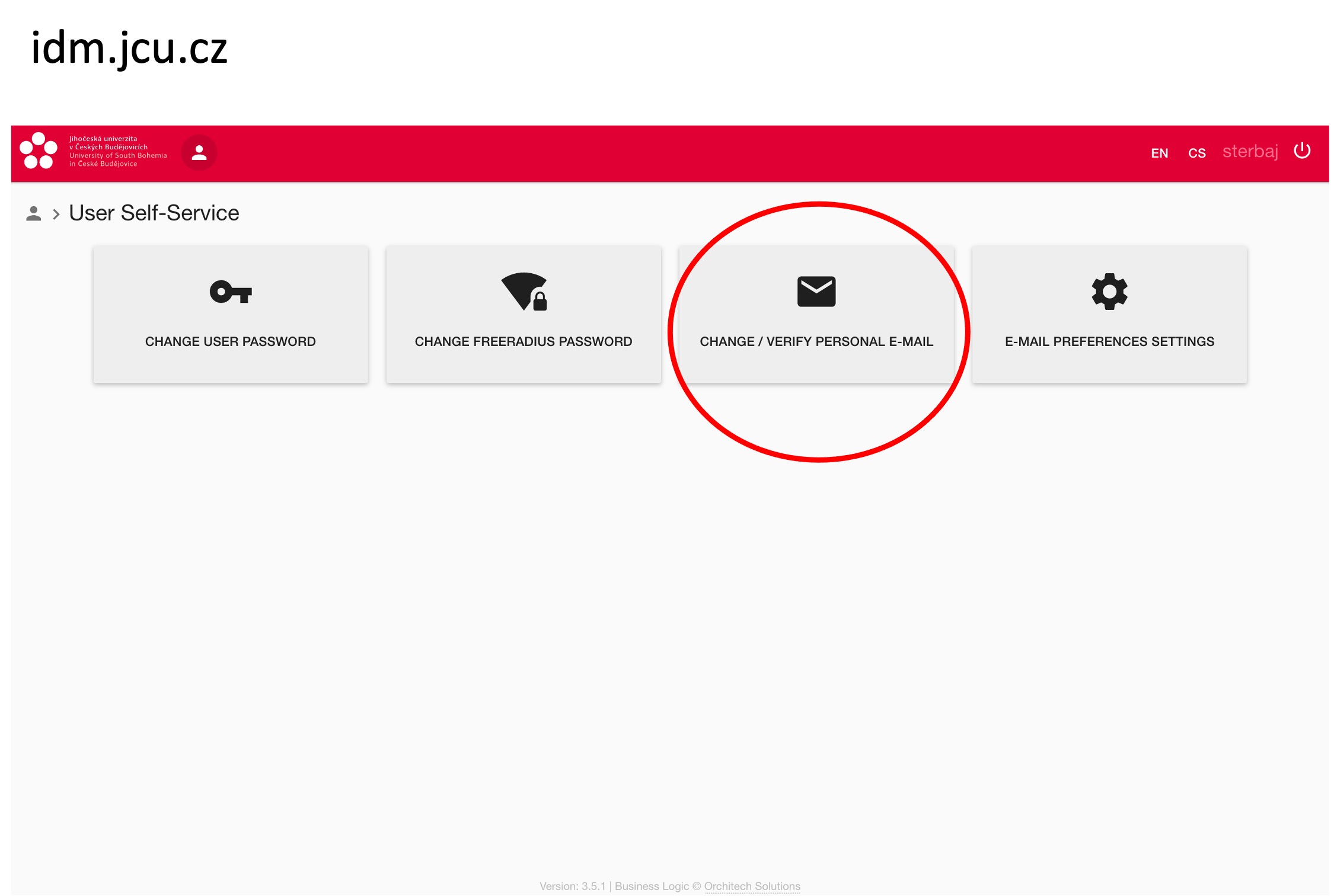
Students working on their MSc thesis in Linz - you must submit the assignment of the Master's thesis also at USB (not only at JKU), and you must apply for the state exam and defence also at USB (even though you do it at JKU), and you must submit your thesis before the defence also at USB.
Constitution of the state exam committee
The state exam committee will consist of at least four members, and at least one will always be from the sister university. The supervisor will be a full member of the state exam committee (according to Linz rules).
For the state exam organised at USB, a committee member from JKU will examine the subject of General Chemistry.
For the state exam organised at JKU, the committee member from USB will examine the subject Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.
Student(s) should contact Dr Štěrba/Prof. Grubhoffer and Prof. Müller regarding the members of the committee in advance.
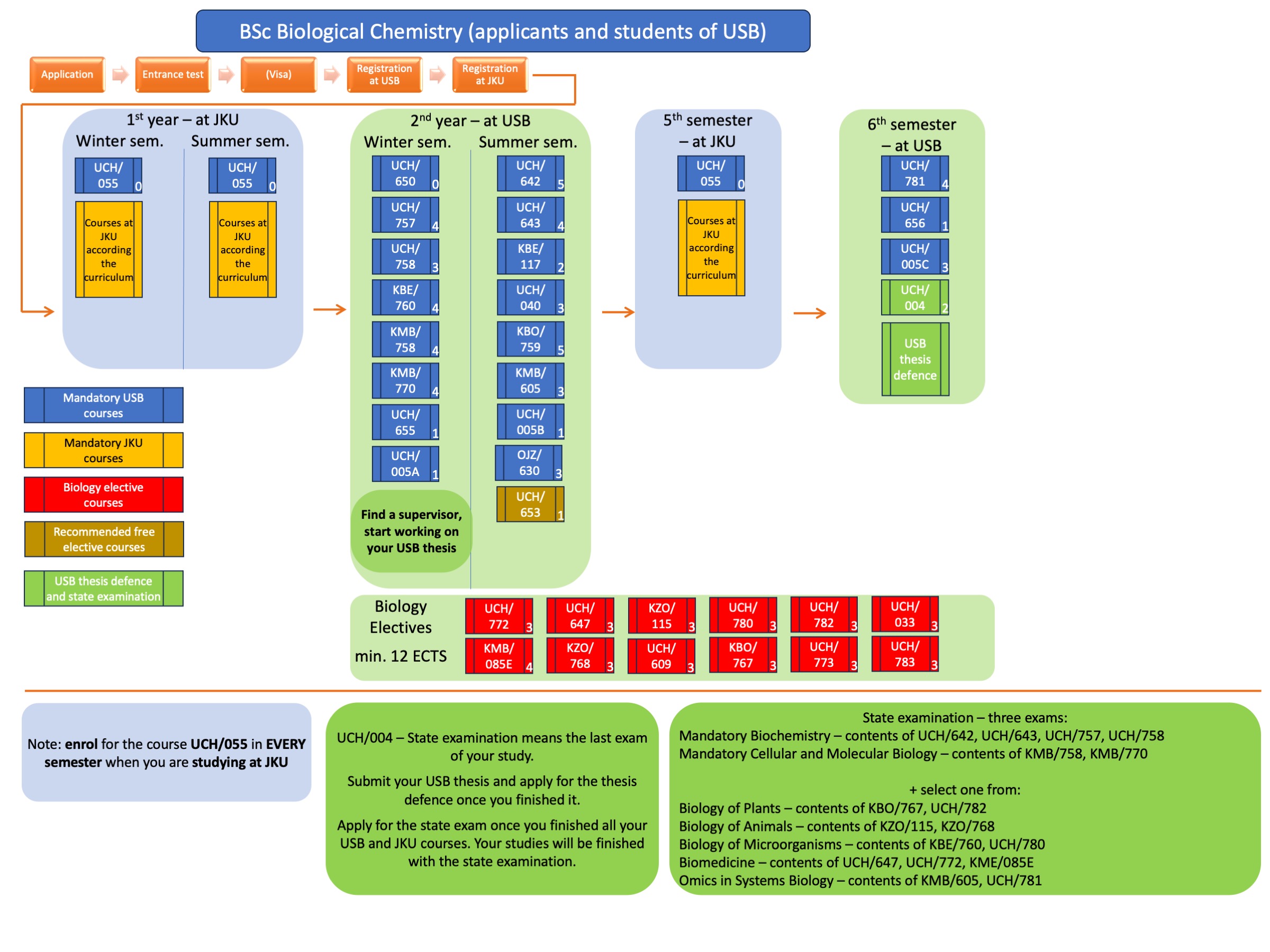
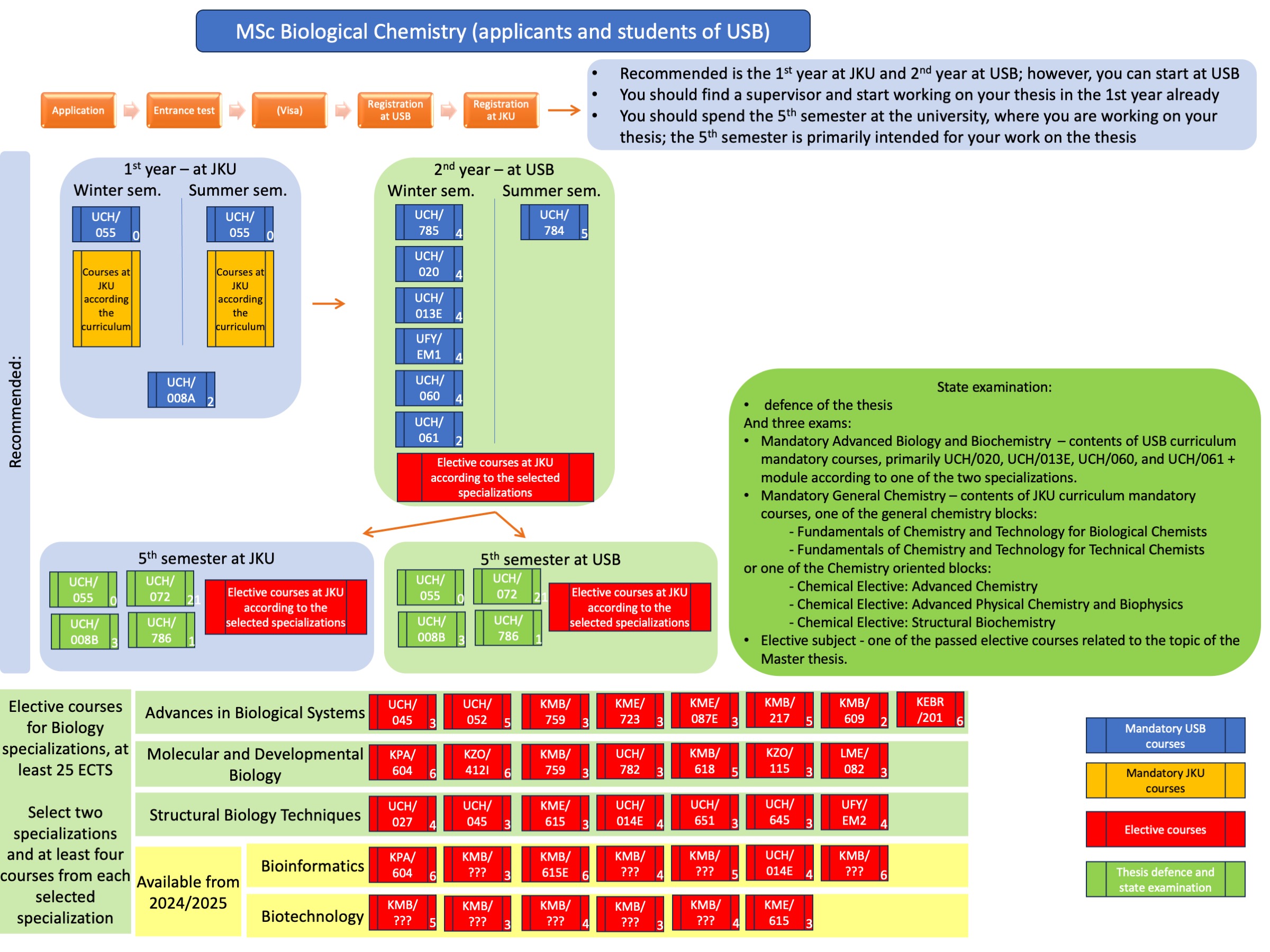
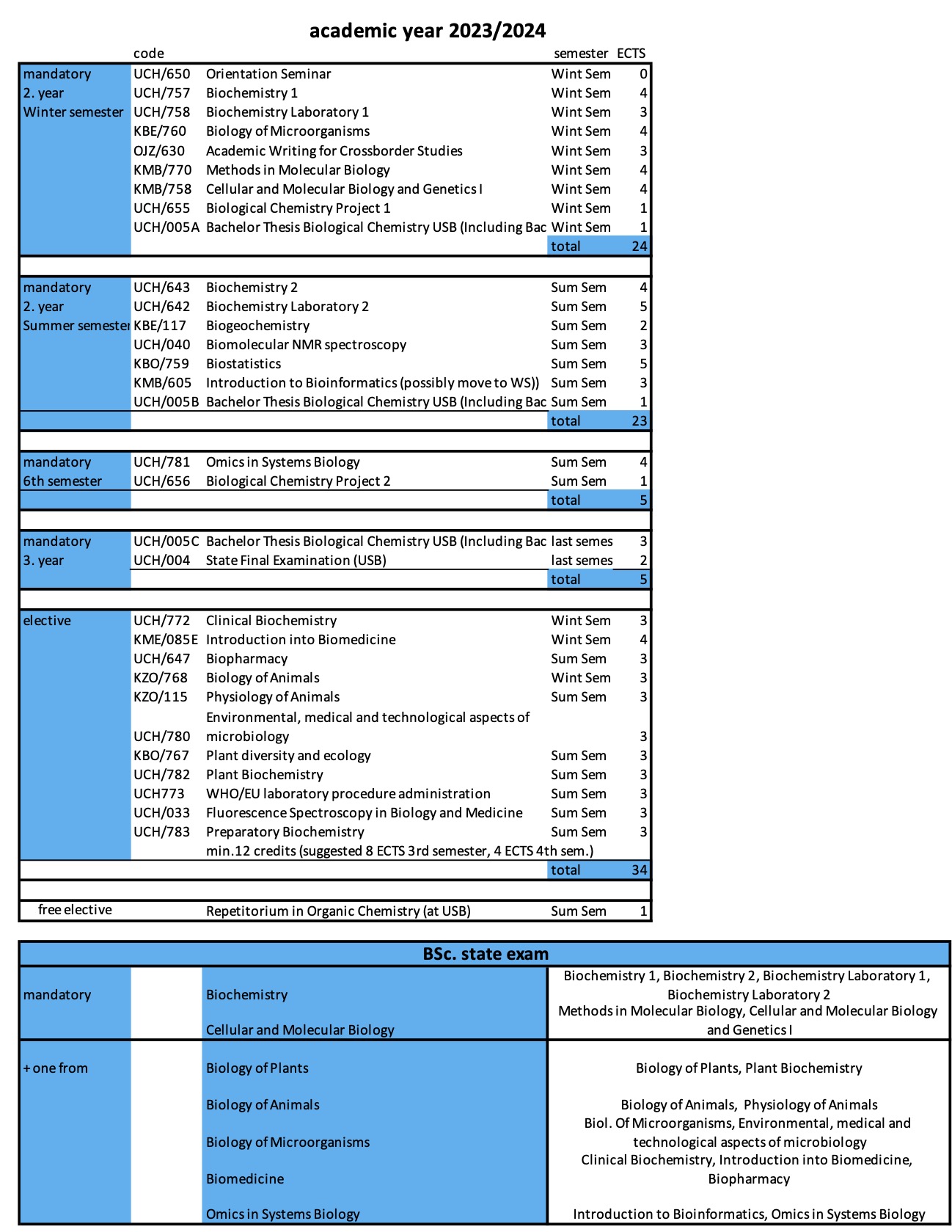
The State Final Examination (SFE) is an oral examination with two parts - a knowledge examination from two compulsory areas and one optional area, and a defence of the master's thesis. A committee usually consisting of at least five members verifies the student's knowledge. A representative of the partner university attends each time. Thus, for students who do their thesis at USB, the JKU representative who examines the General Chemistry subject attends the SFE; for students who do their thesis at JKU, the USB representative who examines the Advanced Biology and Biochemistry subject attends the SFE. The teacher of the subject chosen by the student as an Elective subject, or his/her designated representative, is also a member of the SFE committee.
The SFE consists of two compulsory and one elective areas.
The mandatory areas are:
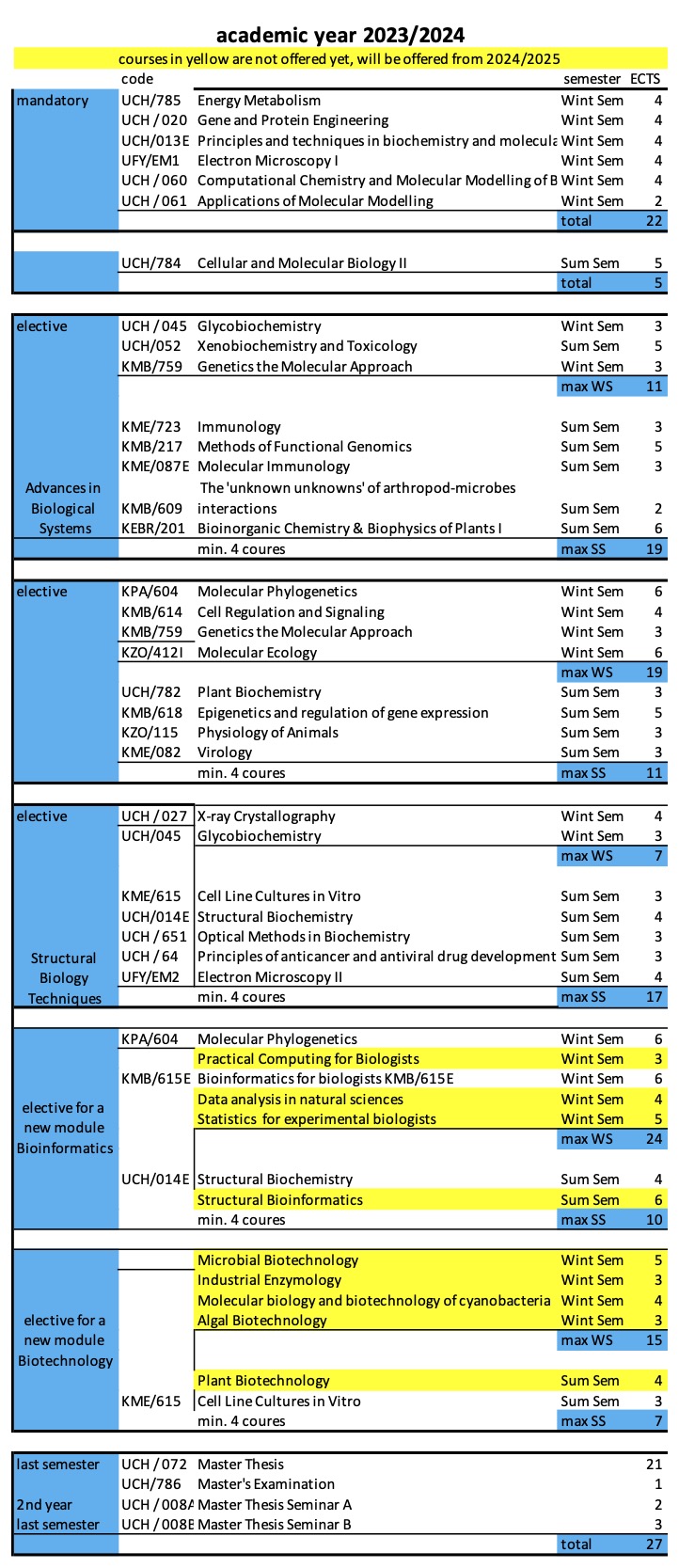
1. UCH/SN11 Advanced Biology and Biochemistry, which represents the biologically oriented part of SFE, especially the content of the lectures from the courses UCH/020 Gene and Protein Engineering, UCH/013E Principles and Techniques in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, UCH/060 Computational Chemistry and Molecular Modelling of Biomolecules and UCH/784 Cellular and Molecular Biology 2, supplemented by one selected biological module (according to the student's specialization):
- Biological Elective: Advances in Biological Systems – lectures UCH/045 Glycobiochemistry, KMB/217 Methods of Functional Genomics, KME/723 Immunology, and UCH/052 Xenobiochemistry and Toxicology;
- Biological Elective: Molecular and Developmental Biology – lectures KMB/614 Cell Regulation and Signaling, KPA/604 Molecular Phylogenetics, KMB/759 Genetics the Molecular Approach, and KMB/618 Epigenetics and regulation of gene expression;
- Biological Elective: Structural Biology Techniques – lectures UCH/027 X-Ray Crystallography, UCH/651 Optical Methods in Biochemistry, UFY/EM1 Electron Microscopy I and UFY/EM2 Electron Microscopy II;
2. UCH/SN36 General Chemistry, which represents the chemically oriented part of the SFE. The student chooses one of the chemistry areas according to his/her specialisation, covering either Fundamentals of Chemistry and Technology or one of the chemically oriented modules chosen in Linz. Chemistry Fundamentals subject:
- Fundamentals of Chemistry and Technology for Biological Chemists
- Fundamentals of Chemistry and Technology for Technical Chemists
The reason for the introduction of these two courses is to allow students to transfer between Biological Chemistry and Technical Chemistry at JKU, which are very similar, if students complete some of the required courses (bridge subjects). From the point of view of knowledge, the content of both of these SFE subjects is the same, the two names are given only for formal reasons and cover mainly knowledge from Organic Chemistry III, Advanced Instrumental Analysis, Spectroscopy and Structural Elucidation II.
The elective part of the SFE consists of the course UCH/SN12 Biological Chemistry Masters Elective, which is chosen by the students from the courses taken during their master's studies at the university where they worked on their thesis, and which is related to their thesis and thus represents a verification of the students' theoretical knowledge.
Furthermore, upon successful completion of the SFE, the student is given credit for the course UCH/786 Master's Examination.
Recommended elective subjects at USB:
Bioenergetics
Gen and Protein Engineering
Enzymology
Protein Chemistry
Electron Microscopy
X-ray Crystalography
Fluorescence spectroscopy
Cell Signaling
Computational Chemistry
Glycobiochemistry
Xenobiochemistry
Immunology
Biopharmacy
Virology
Bioinformatics
Molecular Phylogeny